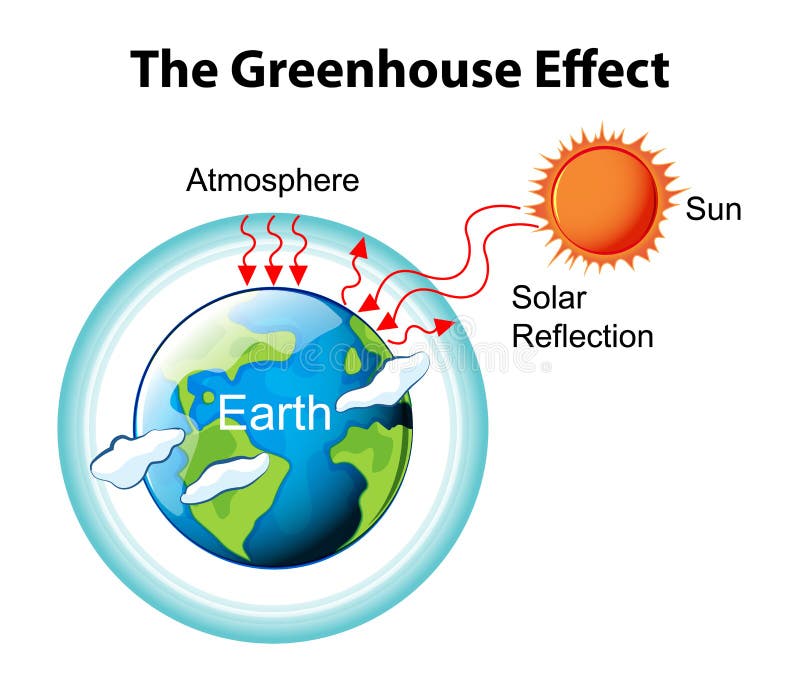
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear French mathematician Joseph Fourier isThe greenhouse effect occurs when certain gases in the Earth's atmosphere (the air around the Earth) trap infrared radiationThis makes the planet become warmer, similar to the way it makes a greenhouse become warmer The greenhouse effect is caused by greenhouse gases;This effect is called globalwarming By burning fossil fuels, industrial societies like Western Europe and the Americas are putting carbon dioxide into the atmosphere at a faster rate than plants can absorb it This is adding to the greenhouse effect, hence an enhanced greenhouse effect occurs, and this may be causing global warming
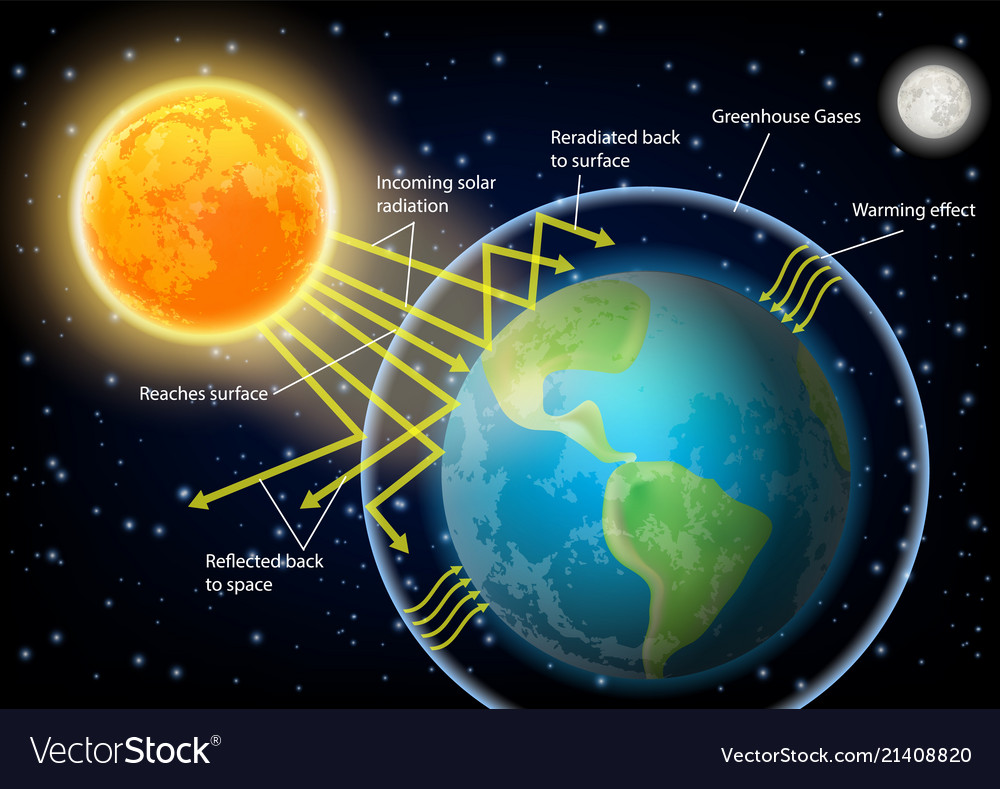
Greenhouse Effect Diagram Royalty Free Vector Image
Simple enhanced greenhouse effect diagram
Simple enhanced greenhouse effect diagram-The "Greenhouse Effect" A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the "greenhouse effect" The greenhouse effect worksAnthropogenic or human release of carbon dioxide is what is contributing to an additional or enhanced greenhouse effect Footnote




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature
Enhanced greenhouse effect The concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has increased in the last 0 years The concentration of carbon dioxide in Greenhouse gases absorb energy, slowing or preventing the loss of heat to space These gases act like a blanket, making Earth warmer than it would otherwise be and throwing off the energy balance of the planet This is known as the greenhouse effectGlobal warming is attributed to the enhanced greenhouse effect This is caused by the increased concentration and effect of greenhouse gases, such as
A short video explaining the enhanced greenhouse effecthttps//wwwspendmoretimeinthewildcoukHere at Spend More Time InA diagram showing how the greenhouse effect works on Earth Although the greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, there are concerns with something known as the enhanced greenhouse effect The enhanced greenhouse effect is generally what is being talked about when people refer to the greenhouse effect and climate change Burning fossil fuels such as natural gas, coal, oil, and gasoline raises the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, and carbon dioxide is a major contributor to the greenhouse effect
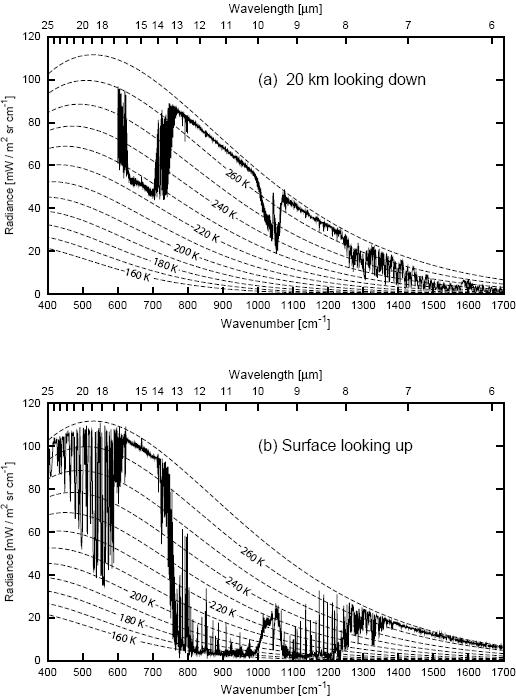
The Greenhouse Effect The picture below shows the greenhouse effect Light from the sun passes through the atmosphere and is absorbed by the Earth's surface, warming it Greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, act like a blanket, trapping heat near the surface and raising the temperature It is a natural process that warms the planetThe answer lies in the greenhouse effect — gases in our atmosphere (including CO 2, CH 4 (methane) and H 2 O water vapor) trap much of the emitted heat and then reradiate it back to Earth's surface This means that the energy leaving our planet from the top of the atmosphere is less than one would expect given the known temperature of ourWHAT IS THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action, however, has increased the presence of these




Global Warming Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Lesson



Greenhouse Effect Basics Warm Earth Cold Atmosphere
Greenhouse gases keep our planet livable by holding onto some of Earth's heat energy so that it doesn't all escape into space This heat trapping is known as the greenhouse effect Just as too little greenhouse gas makes Earth too cold, too much greenhouse gas makes Earth too warm Over the last century, humans have burned coal, oil, andThe effect is larger than in our simple model,Greenhouse effect and evidence of enhanced greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect The Earth's atmosphere acts like a greenhouse, trapping some of the energy from the Sun and keeping the planet warm




Graphical Illustration Of Natural And Anthropogenic Greenhouse Effects Download Scientific Diagram




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect En la gráfica se comparan los cambios en la temperatura de la superficie global (línea roja) y la energía del Sol que recibe la Tierra (línea amarilla) en vatios (unidades de energía) por metro cuadrado desde 10 However, the actual existence of a greenhouse effect was already known In 14, Joseph Fourier had written that 'the temperature of the Earth can be augmented by the interposition of the atmosphere, because heat in the state of light finds less resistance in penetrating the air, than in repassing into the air when converted into nonluminous heat'How the greenhouse effect works It's thought that the buildup of greenhouse gases impacts on global temperature in two ways The gases allow more of the sun's rays to enter the atmosphere



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
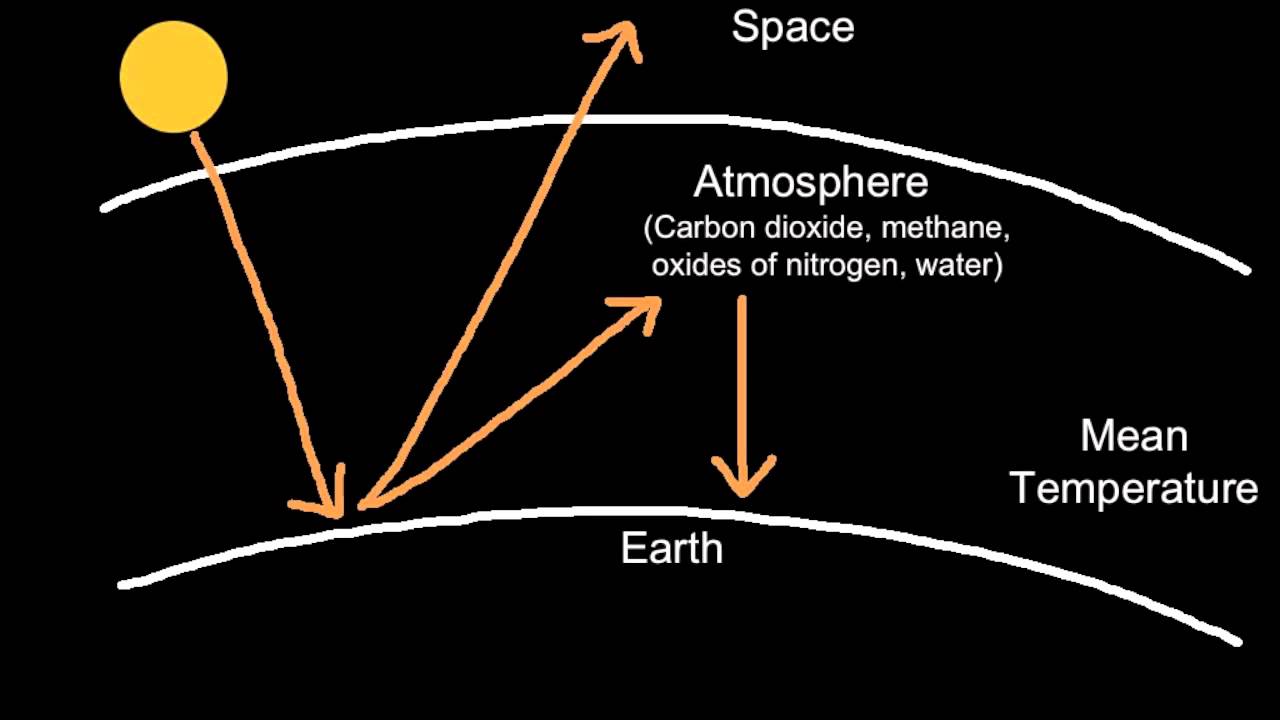



5 2 3 Explain The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Youtube
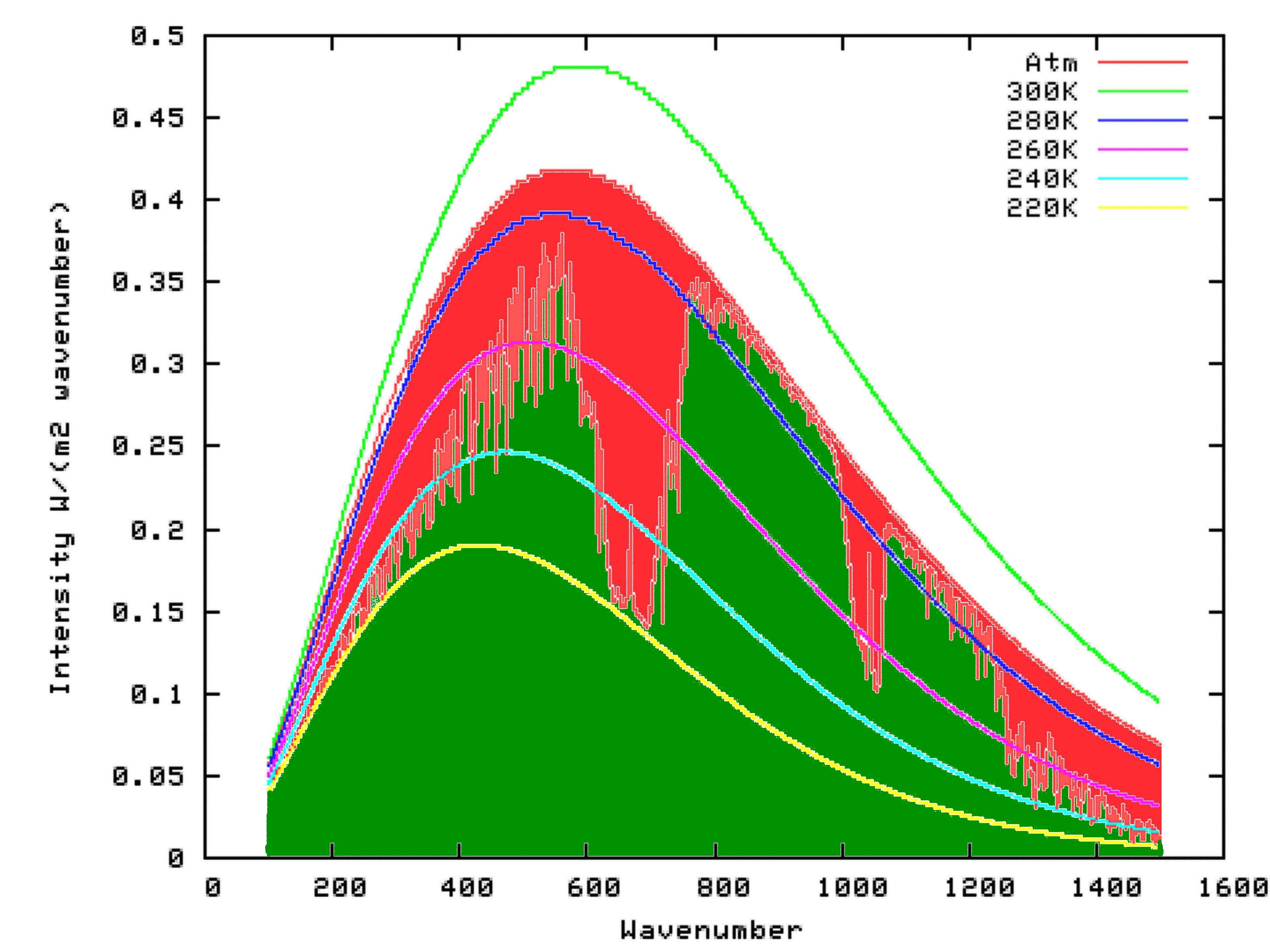
The greenhouse effect has supported life on the earth for millions of years Today, however, the greenhouse effect is growing stronger as human activities such as deforestation and fossil fuel use release more and more greenhouse gases into the atmosphere This traps greater amounts of the sun's radiation, which contributes to rising temperatures, also known as global warmingGlobal surface temperature increased 074 ± 018 °C during the 100 years ending in 05The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) concludes "most of the observed increase in globally averaged temperatures since the midtwentieth century is very likely due to the observed increase in greenhouse gas concentrations"via an enhanced greenhouse effectFigure 715 gives a total radiative forcing of 25 W m2 from increases in greenhouse gases since 1850 From our simple model, this forcing implies a change DTo = 08 K in the Earth's surface temperature, somewhat higher than the observed global warming of 06 K Simulations using general circulation models indicate values of l in the range 0314 K m2 W1 depending on the model;
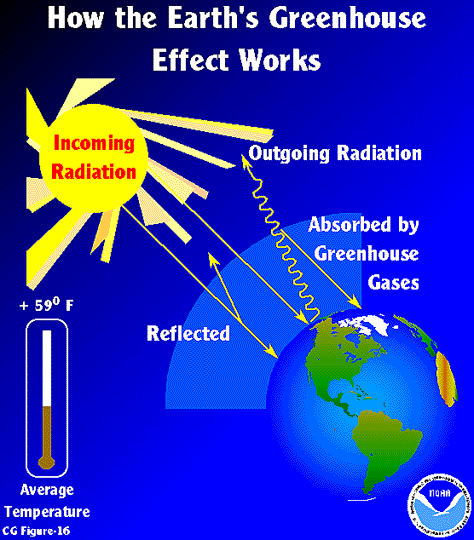



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
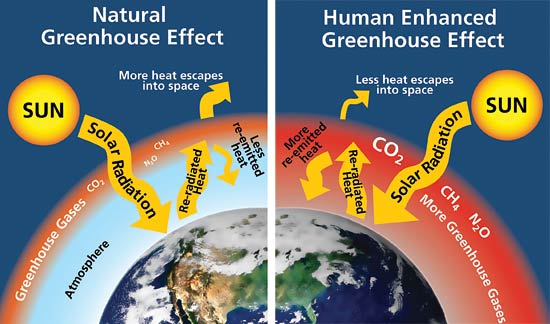



Greenhouse Effect And Anthropogenic Warming Mrgeogwagg
The greenhouse effect is the term used to describe the warming of the Earth The diagram shows this If there were no greenhouse gases the Earth would be a frozen, lifeless ball in space, but too many gases and the planet warms up causing dangerous climate changeThe greenhouse effect is a warming of the earth's surface and lower atmosphere caused by substances such as carbon dioxide and water vapour which let the sun's energy through to the ground but impede the passage of energy from the earth back into space A simplified diagram illustrating the greenhouse effect (based on a figure in the 07 IPCCAbstract A distinction is made between the greenhouse effect and the increased or enhanced greenhouse effect The radiation budget of the atmosphere is reviewed, and a simple balanced model is designed permitting the calculation of a mean surface and a




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students
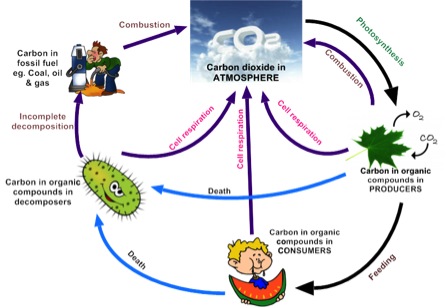



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Biology4ibdp
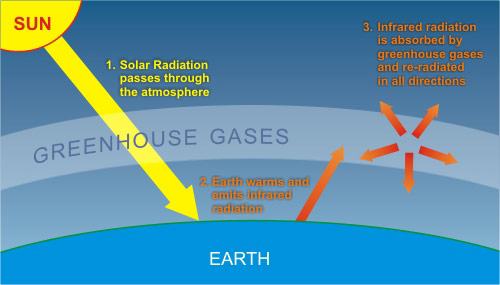
The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to existThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it The intensity of downward radiation – that is, the strength of the greenhouse effect – depends on the amount of greenhouseThe most important greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide(CO 2), and




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Showing How The Greenhouse Effect Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image
Greenhouse Effect Teaching Box This teaching box provides resources related to the greenhouse effect It will help you teach how the greenhouse effect works, and how it prevents Earth from becoming a frozen ball of ice!/ The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect 2 Student Worksheet NEW Click The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect 2 Student Worksheetpdf link to view the file Students explore natural causes of climate change and human contributions of greenhouse gases to our atmosphereTeaching Boxes are collections of classroomready and standardsaligned activities, content, and multimedia that build




Greenhouse Gases And Global Warming Ballotpedia




Climate Change Science And Impacts Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems
Summary The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that warms the Earth's surface and makes life on our planet possible However, human activities, especially the burning of fossil fuels, are increasing the levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and causing the Earth to warm at a faster and higher rate Through demonstrations and simple models, students gain an understanding of the enhanced greenhouse effect The Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring phenomenon in which the specific gases in the atmosphere of the Earth trap heat from the sun (see The Greenhouse Effect Diagram attachment) Typically, our atmosphere absorbs just the right amount of heat so that living things can surviveLearn more Download for free Royaltyfree stock vector ID Natural and human enhanced Greenhouse effect diagram showing solar radiation and planet Earth Global warming, climate change Education for kids Cartoon vector illustration in flat style I By Inna Bigun




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
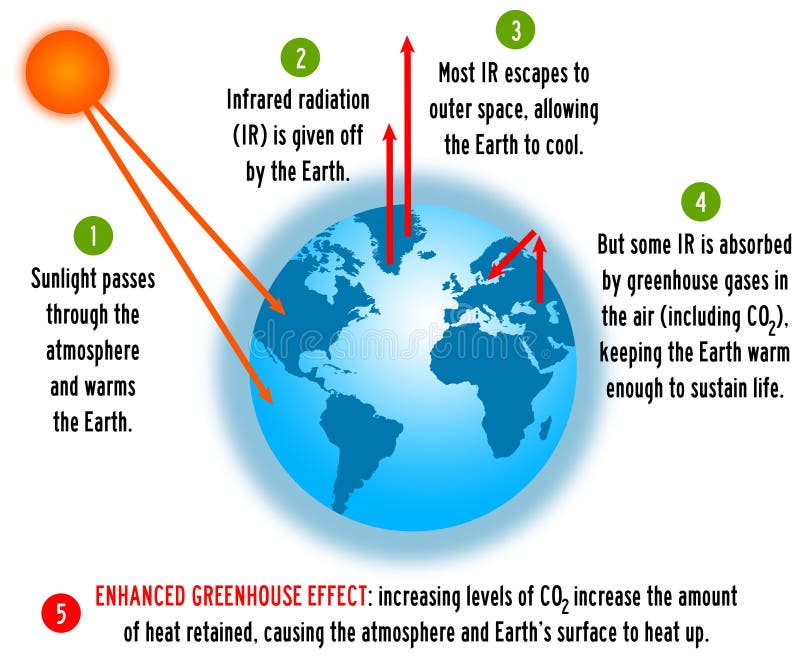



Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 149 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
The greenhouse effect Without the greenhouse effect the mean temperature on Earth would be 18°C and there would be very little or no life So the greenhouse effect itself is a good thingAny change in the environment leading to additional and enhanced changes in that system is the result of a positive feedback mechanism Alternatively, if a change in the environment leads to a compensating process that mitigates the change it is a negative feedback mechanism and humanmade aerosols may confound the effect of greenhouse gasThe process of the greenhouse effect is quite simple and straightforward The sun emits energy toward earth's atmosphere Gases absorb heat and radiate some of it back to earth's atmosphere, making the surface temperature warmer The earth radiates energy from the sun (as infrared or longwave radiation) back to space




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts



Q Tbn And9gcs3 Vn3xnwnq9ifctpyrsa2ofh2ymxfw2rxlcy7frr77uflqr Usqp Cau
Greenhouse gases let the sun's light shine onto the Earth's surface, but they trap the heat that reflects back up into the atmosphere In this way, they act like the insulating glass walls of a greenhouse The greenhouse effect keeps Earth's climate comfortable Without it, surface temperatures would be cooler by about 33 degrees Celsius The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxidesThe diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect How the greenhouse effect works Electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's atmosphere




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
Radiative forcing is the change in energy flux in the atmosphere caused by natural and/or anthropogenic factors of climate change as measured by watts / metre 2 It is the scientific basis for the greenhouse effect on planets, and plays an important role in computational models of Earth's energy balance and climateChanges to Earth's radiative equilibrium that cause temperatures toGreenhouse effect Step 1 Solar radiation reaches the Earth's atmosphere some of this is reflected back into space Step 2 The rest of the sun's energy is absorbed by the land and the oceans, heating the Earth Step 3 Heat radiates from Earth towards spaceEnhanced Greenhouse effect 'Greenhouse gases' are actually crucial to keeping our planet at a habitable temperature, without them the Earth would be about minus 17 degrees!




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay




Climate Change And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
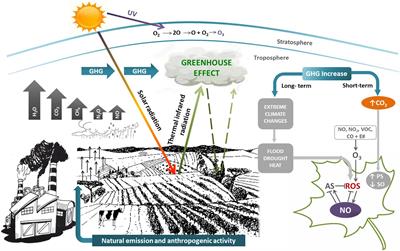



Frontiers Climate Change And The Impact Of Greenhouse Gasses Co2 And No Friends And Foes Of Plant Oxidative Stress Plant Science
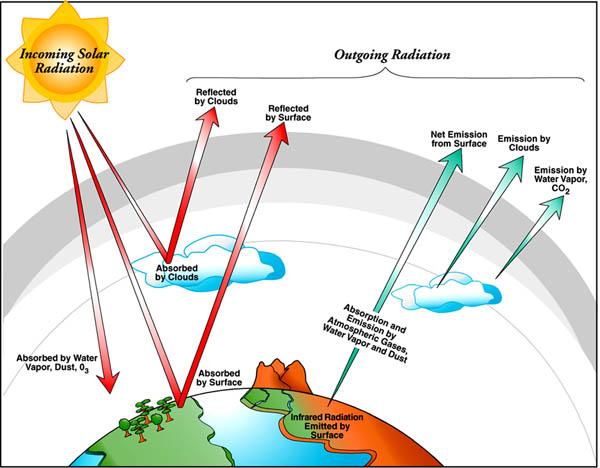



Lab 2 Climate And Earth S Energy Balance
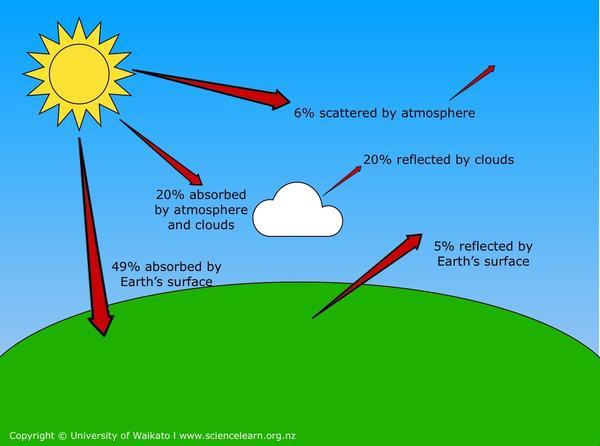



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub
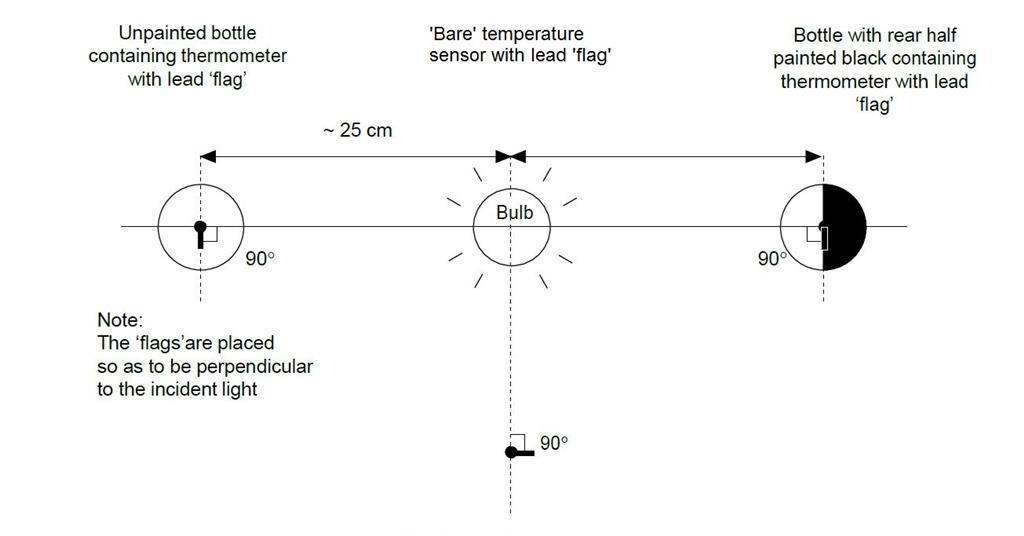



Modelling The Greenhouse Effect Experiment Rsc Education




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Natural Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Diagram Stock Vector Royalty Free
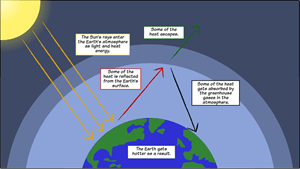



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Global Warming Lesson Plan




Igcse Biology 17 4 15 Understand How An Increase In Greenhouse Gases Results In An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect And That This May Lead To Global Warming And Its Consequences




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases With Examples




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com
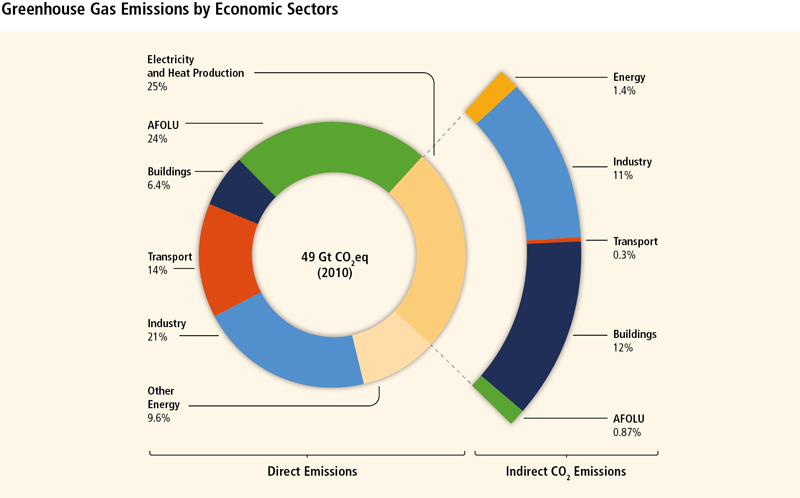



Causes Of Climate Change And Sea Level Rise Coastadapt




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
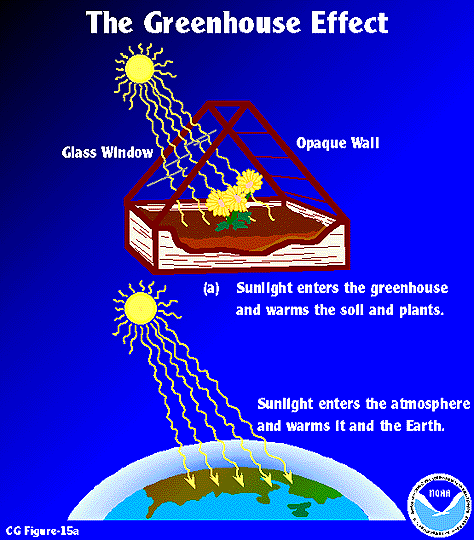



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja



The Greenhouse Effect
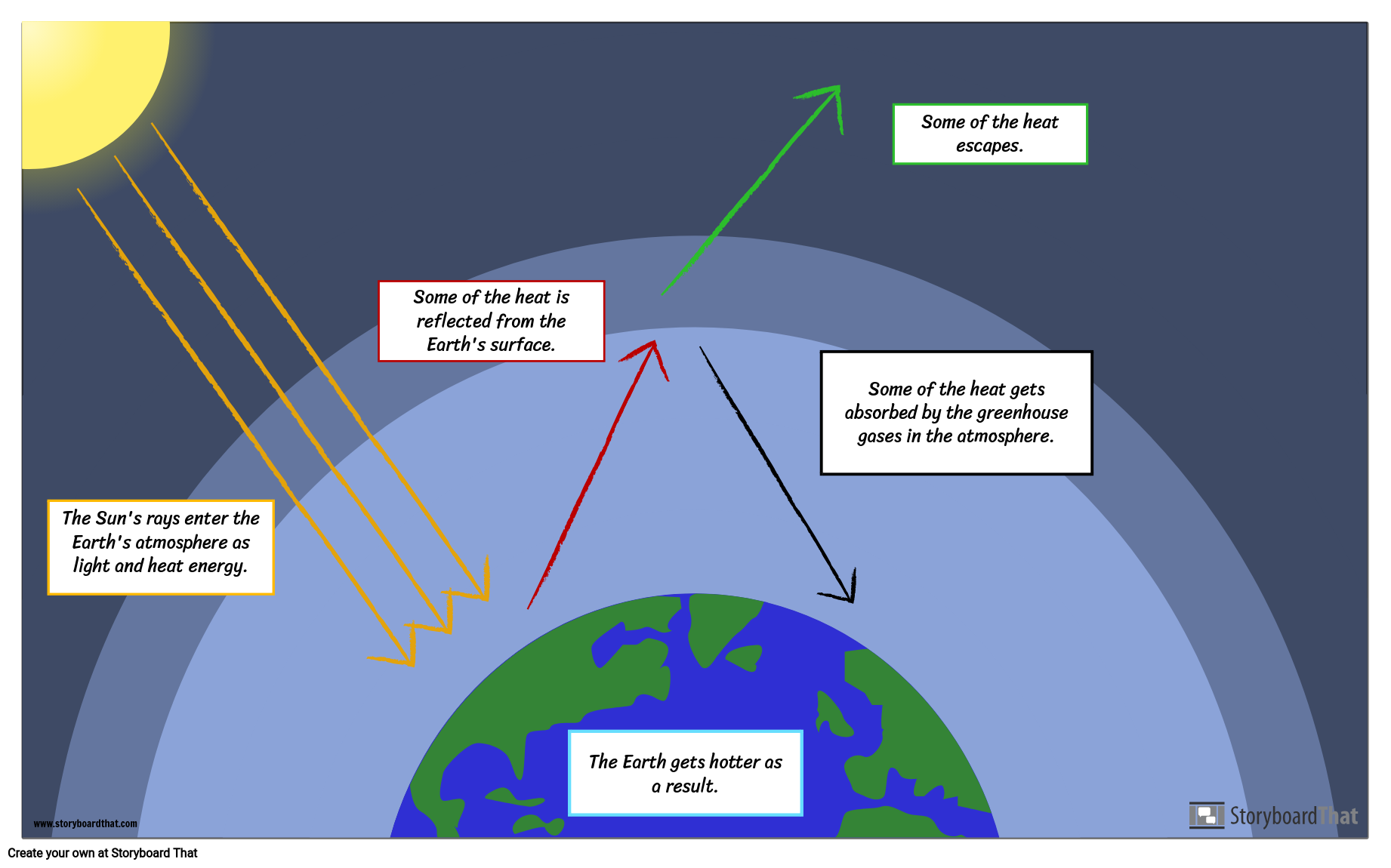



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Global Warming Lesson Plan
.png)



Greenhouse Effect Energy Education




The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
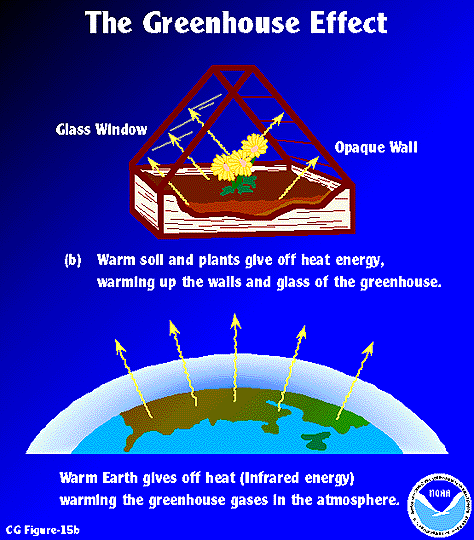



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
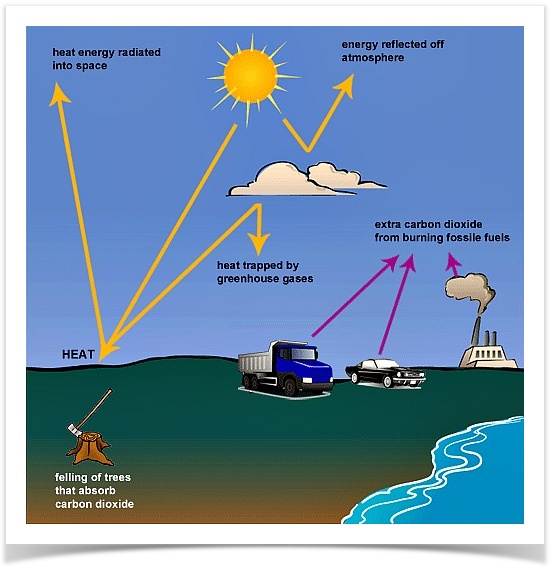



Graph Writing 162 Greenhouse Gases Trap Energy From The Sun




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering



1
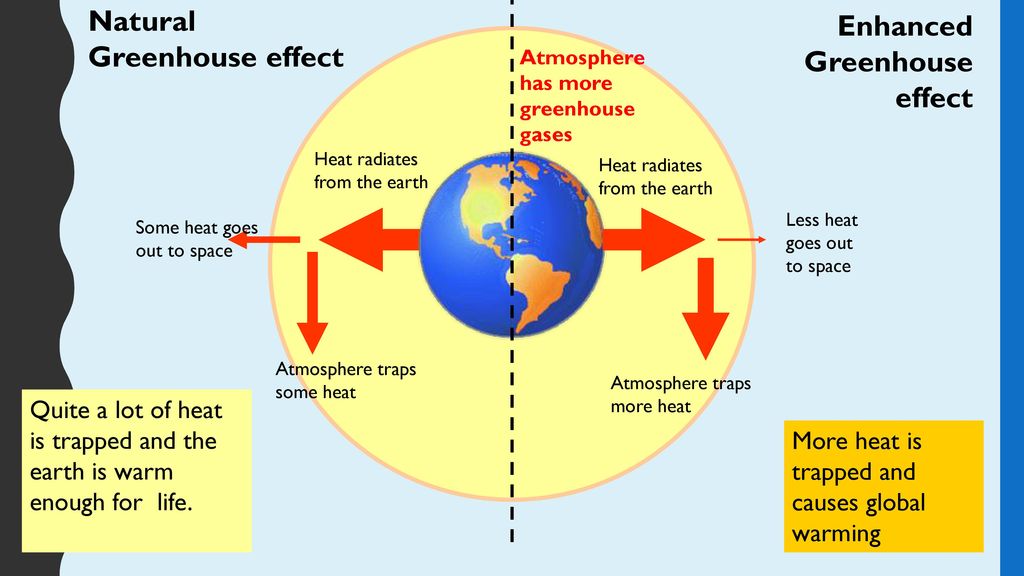



Global Warming General Studies Unit F Ppt Download




What Is An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Universe Today
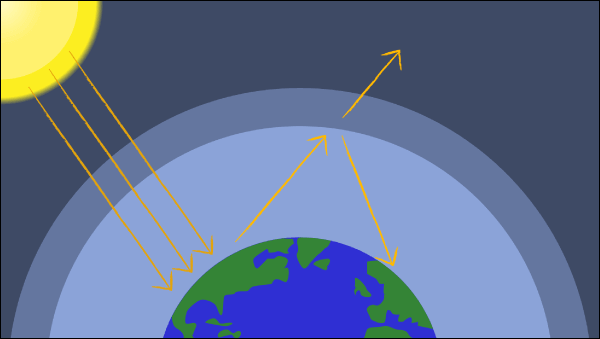



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Global Warming Lesson Plan




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
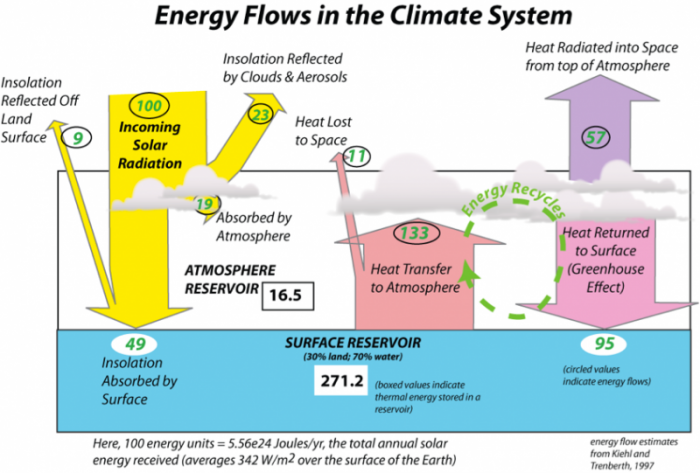



The Greenhouse Effect And The Global Energy Budget Earth 103 Earth In The Future



The Greenhouse Effect And The 2nd Law Of Thermodynamics



Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 149 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly



Ib Biology Notes 5 2 The Greenhouse Effect



Www Chicagobotanic Org Downloads Nasa Unit 1 Grades 7 9 Activity 1 1 Understandingthegreenhouseeffect Pdf



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau



How Do We Know More Co2 Is Causing Warming
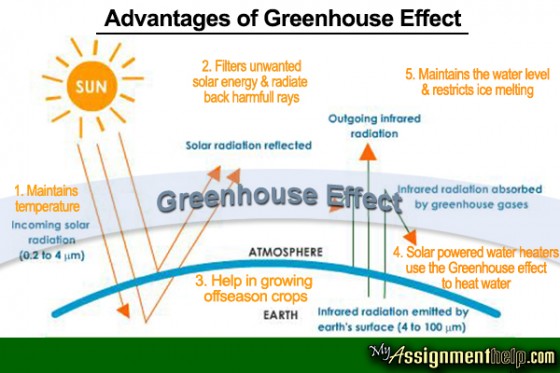



The Greenhouse Effect Know The Advantages And Disadvantages




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram



1
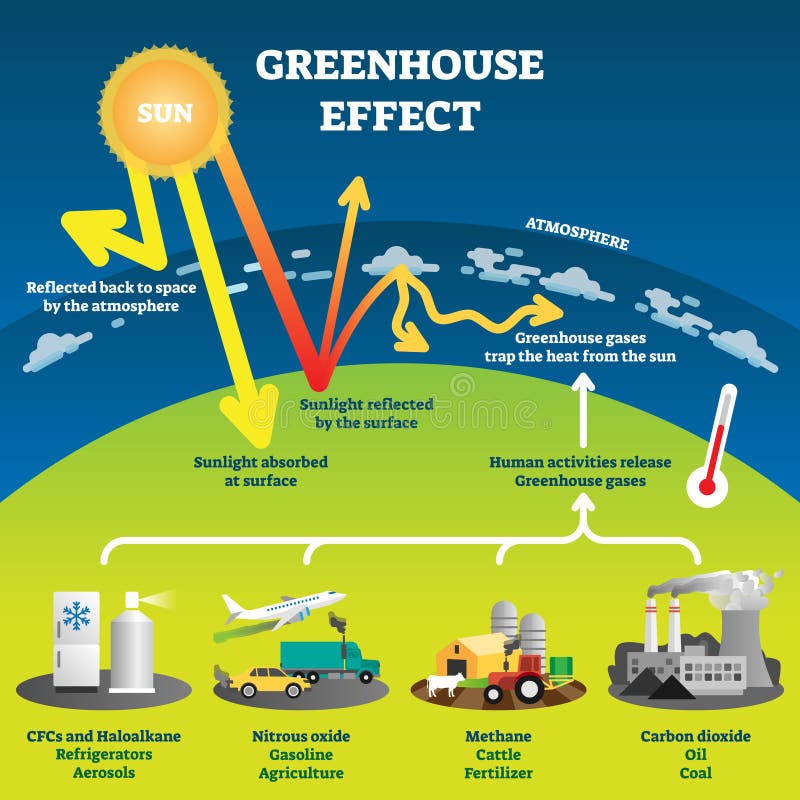



Greenhouse Stock Illustrations 914 Greenhouse Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Royalty Free Vector Image




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects
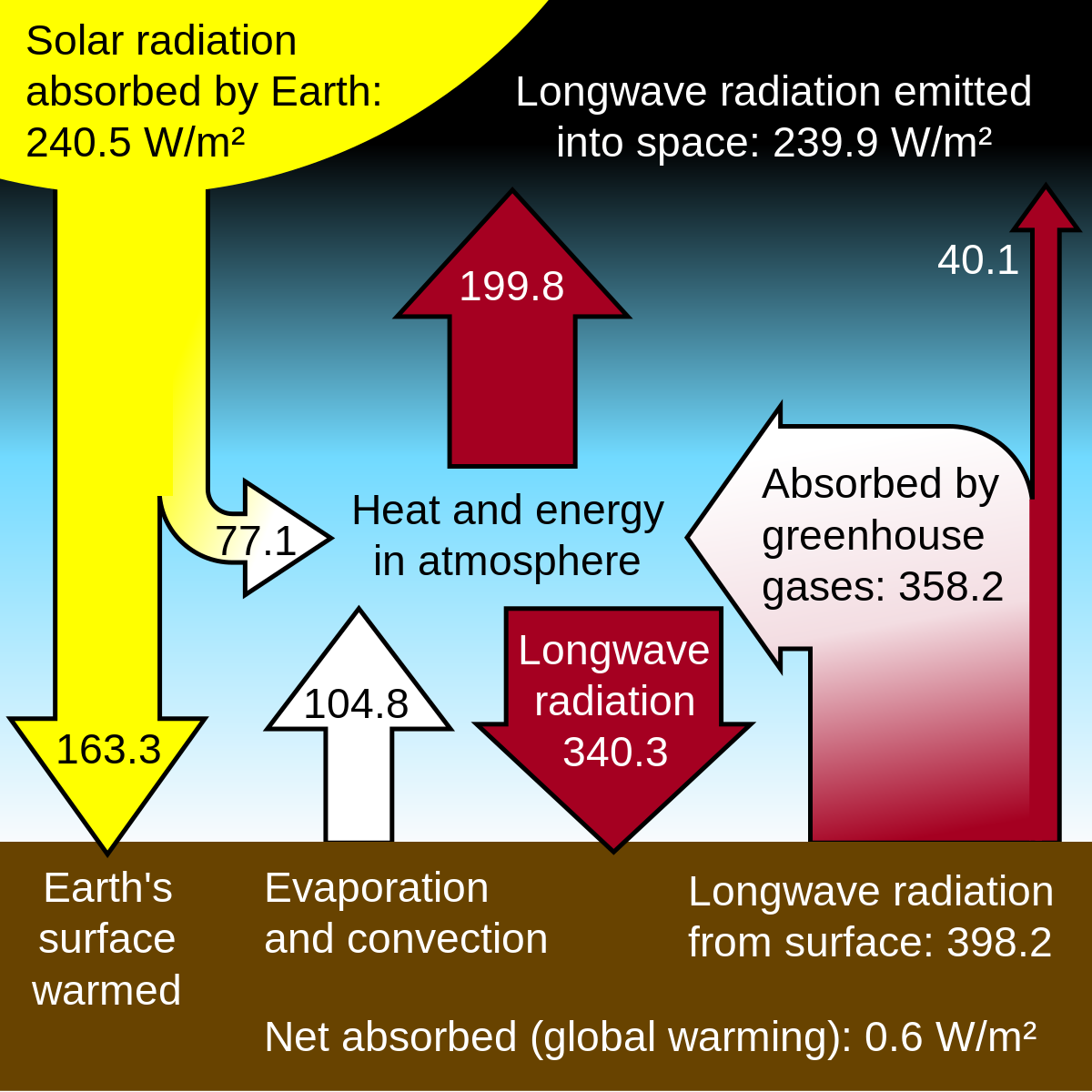



Greenhouse Effect Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia



Global Warming




Global Warming For Kids A Simple Explanation Of Climate Change




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Effect Teaching Box Ucar Center For Science Education



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Effect Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




A Picture Of Climate Change Is Worth 1 000 Words Simple Climate




Greenhouse Effect And Anthropogenic Warming Mrgeogwagg




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
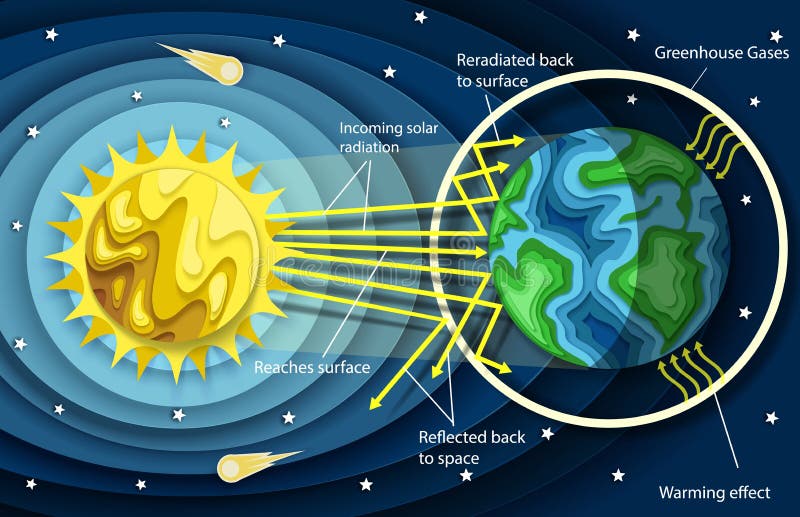



Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 149 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
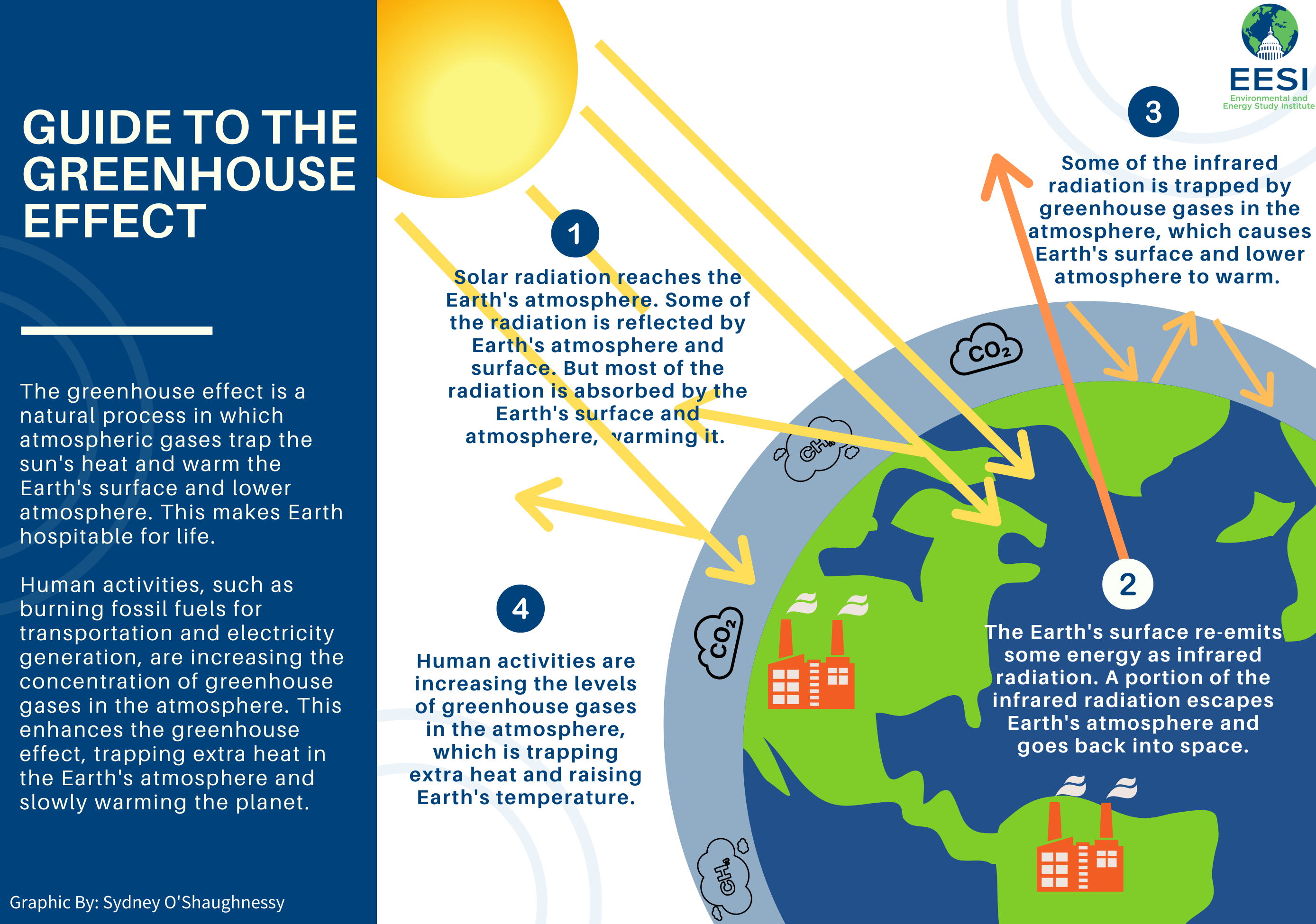



Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




6 A Simplified Diagram Illustrating The Greenhouse Effect Based On A Download Scientific Diagram



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature




Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet




How To Draw A Diagram Of Green House Effect Global Warming Easy Youtube




The Greenhouse Effect Explained
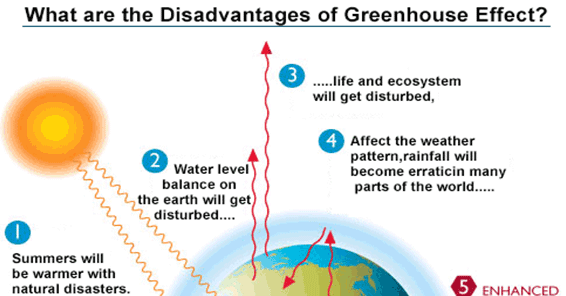



Disadvantages Of Greenhouse Effects Myassignmenthelp Com




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com




Greenhouse Effect
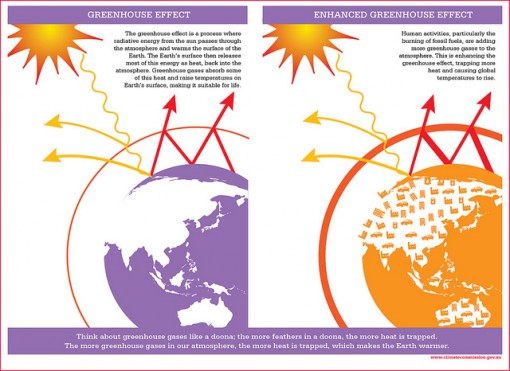



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Conserve Energy Future




Teaching Climate Change American Federation Of Teachers



Forests And Climate Change



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿